The Ballistic Coefficient calculator computes the Ballistic Coefficient a factor representing the effect of air resistance on a ballistic projectile.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- M- the mass of the projectile
- Cd- empirically derived value for the projectile
- A - the cross-sectional area of the projectile
Ballistic Coefficient (BC): The calculator computes the Ballistic Coefficient in units of kg/m2.
Common Drag Coefficients(Cd)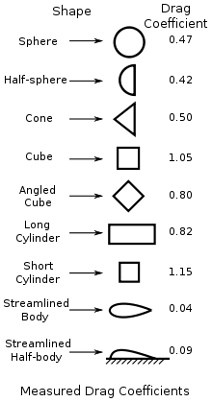
The Math / Science
Ballistics is the science of mechanics behind projectile flight, behavior of objects during un-powered trajectories, and the effects of projectiles. Ballistics predicts the flight of objects such as bullets, free-falling bombs, rockets, or similar objects whose path is determined primarily by gravity and air resistance. The ballistic coefficient (BC) of an object defines the effect of air resistance on the object's flight. BC is inversely proportional to the negative acceleration of the ballistic object. The projectile, the ballistic object possesses drag, the BC measures the extend of the drag's effect on the object.
BC is a function of mass, diameter, and drag coefficient and also relates to the aerodynamics of the projectile. Ballistic coefficient has units of mass per area (lb/in2 or kg/m2)
The formula for the Ballistic Coefficient is:
`BC = M/(C_d*A)`
where:
- BC = Ballistic Coefficient
- M = Mass of Projectile
- Cd = Coefficient of Drag
- A = Cross-sectional Area of Projectile

- Sectional Density: Computes the factor used in the computation of the ballistic coefficient called sectional density.

- Bullet Ballistic Coefficient: Computes factor that represents a bullet's ability to overcome air resistance in flight.
- Ballistic Coefficient from Bullet's Mass, Diameter and Form Factor: Estimates the ballistic coefficient from the mass, diameter and form factor
- Miller Twist Rule: Computes the optimal barrel twist rate for stabilizing a bullet's flight given the bullet's diameter, length and mass.
- Taylor Knock-out Factor: Calculates a factor indicating the power of a round,.
- Greenhill Formula for Optimal Rifling Twist Rate: calculate the optimal barrel twist rate for stabilizing a bullet's flight given the bullet's diameter, length, specific gravity and velocity.
- Bullet Flight Range: Computes the maximum range (horizontal distance) traveled by a bullet based on the muzzle velocity, elevation angle and shooter height.
- Muzzle Energy of a Projectile: Calculates the kinetic energy in a bullet immediately after leaving the barrel given the bullet's mass and velocity.
- Recoil Velocity of a Gun: Computes the velocity at which a gun will move in the opposite direction in relation to the projectile that it fired.
- Cost per Round: Computes cost per round of ammunition based on the cost of a container of cartridges and the number of rounds in the container.
 Rifle Sight Correction Angles: Computes the Minutes of Angle corrections for rifle sights.
Rifle Sight Correction Angles: Computes the Minutes of Angle corrections for rifle sights.- Shotgun Shell Reloading Cost: Computes the cost to reload used shotgun shells (hulls) with powder, shot, wads and primers.
- Shotgun Shell Loading Cost: Computes the cost to load new pre-primed shells (hulls) with power, shot and wads.
- Metal Ball Weight: Computes the mass (weight) of a spherical metal (e.g., steel) ball based on the size (diameter).
- Metal Cylinder Weight: Computes the mass (weight) of a metal cylinder based on the size (diameter and length).


